Definition of Assistive Technology
Assistive technology refers to any device, equipment, or system that enhances the independence, functioning, and overall quality of life for individuals with disabilities. It encompasses a wide range of tools and solutions designed to address specific challenges and promote inclusivity. Assistive technology can take various forms, such as mobility aids, communication devices, sensory enhancements, and computer software.
Its primary goal is to bridge the gap between individuals with disabilities and their environment, empowering them to overcome limitations, access information, communicate effectively, and engage in various activities with greater ease and independence.
One key aspect of assistive technology is its versatility and customization. It recognizes that disabilities come in different forms and affect individuals in unique ways. Therefore, assistive technology solutions are often tailored to meet specific needs, accommodating a wide range of disabilities, including visual, auditory, physical, cognitive, and developmental impairments.
This adaptability enables individuals to personalize their technology to suit their abilities and preferences, ultimately fostering a sense of empowerment and autonomy.
Furthermore, assistive technology plays a crucial role in promoting inclusion and equal opportunities. By breaking down barriers and overcoming limitations, it enables individuals with disabilities to participate actively in education, employment, recreation, and social interactions.
Whether it’s a screen reader that enables someone with visual impairments to access digital content or a prosthetic limb that restores mobility and independence, assistive technology empowers individuals to pursue their goals and aspirations, ensuring they are not excluded or left behind due to their disabilities.
Importance Of Assistive Technology For Individuals With Disabilities
Assistive technology holds immense importance for individuals with disabilities as it serves as a catalyst for their independence, inclusion, and overall well-being. Here are three key reasons why assistive technology is crucial for individuals with disabilities:
Enhancing Independence: Assistive technology provides individuals with disabilities the tools and support they need to accomplish tasks and activities that might otherwise be challenging or impossible. Whether it’s a wheelchair, prosthetic limb, or speech-to-text software, these technologies empower individuals to perform daily activities, navigate their environment, communicate effectively, and access information.
By promoting independence, assistive technology enables individuals to have greater control over their lives and enhances their sense of self-worth and confidence.
Facilitating Inclusion: In a world that is increasingly digital and interconnected, assistive technology plays a vital role in ensuring that individuals with disabilities can fully participate in various aspects of society.
It helps bridge the accessibility gap by providing alternative methods of communication, enabling access to digital content, and promoting equal opportunities in education, employment, and social interactions.
Assistive technology allows individuals with disabilities to express their thoughts, talents, and abilities, breaking down barriers and promoting a more inclusive society.
Improving Quality of Life: Assistive technology has the power to significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with disabilities. It can alleviate pain, enhance mobility, increase access to education and employment, and foster social connections.
By enabling individuals to participate in meaningful activities and engage with the world around them, assistive technology contributes to their physical, emotional, and psychological well-being. It promotes greater autonomy, self-determination, and overall life satisfaction, allowing individuals to pursue their goals and aspirations.
Types Of Assistive Technology - Vision

Assistive technology for individuals with vision impairments encompasses a range of tools and solutions designed to enhance their visual capabilities and improve access to information.
Here are three types of assistive technology specifically tailored for individuals with vision impairments:
Screen Readers: Screen readers are software programs that convert on-screen text into synthesized speech or braille output. These tools enable individuals with vision impairments to access and navigate digital content, including websites, documents, and applications. Screen readers provide auditory cues and descriptions of visual elements, allowing users to interact with computers, smartphones, and other devices independently. They are vital for tasks such as reading emails, browsing the internet, and accessing educational materials, enabling individuals to engage with information and participate in various digital activities.
Magnification Devices: Magnification devices are assistive technologies that enlarge printed text and visual images, making them more accessible for individuals with low vision. These devices can be in the form of handheld magnifiers, stand-mounted magnifiers, or electronic magnifiers (CCTVs). They allow users to adjust the level of magnification and contrast, enhancing the clarity and readability of text and images. Magnification devices enable individuals to read books, newspapers, labels, and other printed materials, as well as view photographs and other visual content with greater ease.
Braille Displays: Braille displays are tactile devices that convert digital text into braille characters. They consist of a series of small, raised pins that can be individually raised or lowered to represent braille letters and symbols. Braille displays allow individuals with visual impairments to read and navigate electronic text, including books, documents, and web pages, using their sense of touch. By providing access to braille output, these devices enable individuals to engage with written information and communicate effectively. Braille displays are often used in conjunction with screen readers to offer a comprehensive and multimodal approach to accessing information.
These are just a few examples of the assistive technology available for individuals with vision impairments. Each technology is designed to address specific needs and preferences, providing individuals with the tools they need to access information, communicate effectively, and engage with the world around them.
Types of Assistive Technology - Hearing
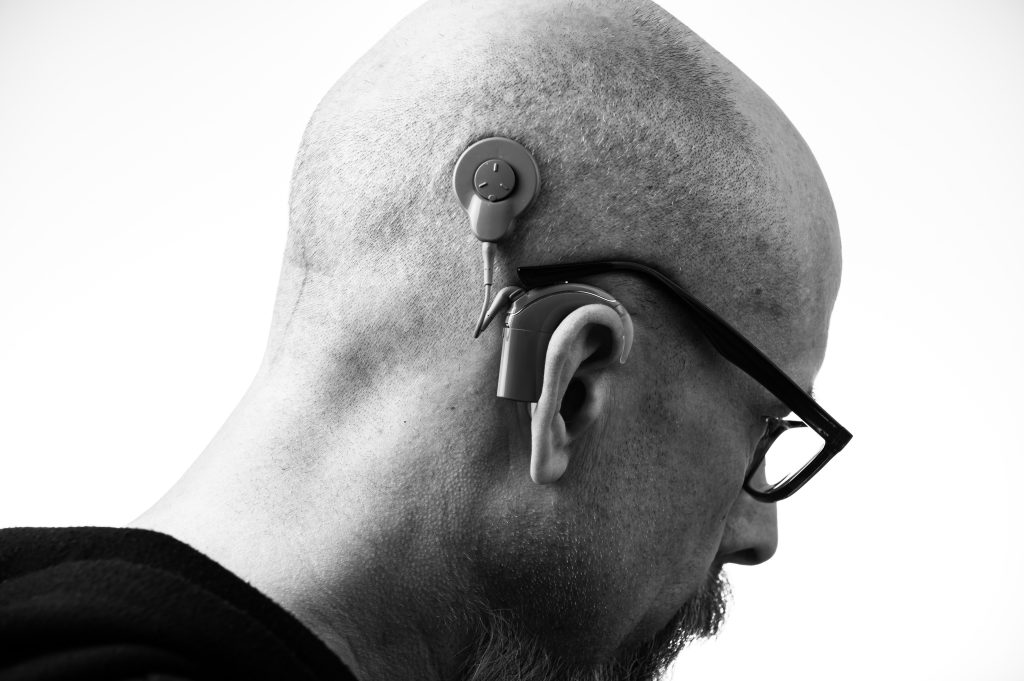
Assistive technology for individuals with hearing impairments includes a range of devices and solutions aimed at enhancing communication, facilitating auditory access, and improving overall hearing experience. Here are three types of assistive technology specifically designed for individuals with hearing impairments:
Hearing Aids: Hearing aids are small electronic devices worn in or behind the ear that amplify sound for individuals with hearing loss. They capture and process sound, making it louder and clearer for the wearer. Modern hearing aids are available in various styles and designs, catering to different degrees and types of hearing loss. They often feature advanced features like noise reduction, feedback cancellation, and connectivity options with other devices, such as smartphones and televisions. Hearing aids significantly improve the ability to hear and understand speech, enabling individuals to actively participate in conversations and engage with their surroundings.
Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs): ALDs are devices that help individuals with hearing impairments overcome background noise and distance-related challenges. They work in conjunction with hearing aids or cochlear implants to enhance sound transmission directly to the individual. ALDs can include systems like personal FM systems, loop systems, infrared systems, and Bluetooth-enabled devices. These technologies improve sound clarity and reduce interference, making it easier for individuals with hearing impairments to hear speech, music, and other audio signals in a variety of settings, such as classrooms, theaters, and public spaces.
Captioning and Real-Time Transcription: Captioning and real-time transcription technologies provide visual representation of spoken content, making it accessible for individuals with hearing impairments. Closed captioning is commonly used for television programs, movies, and online videos, displaying synchronized text that corresponds to the audio. Real-time transcription involves using speech recognition software and skilled transcriptionists to provide immediate, live text display of spoken content, such as in conferences, meetings, and educational settings. These technologies ensure that individuals with hearing impairments can access and understand spoken information, fostering effective communication and equal participation.
These examples highlight some of the assistive technologies available for individuals with hearing impairments. Each technology is tailored to address specific hearing needs, improve auditory access, and promote inclusive communication. By leveraging these technologies, individuals with hearing impairments can overcome barriers, engage in conversations, and experience a more connected and inclusive world.
Types of Assistive Technology - Speech Communication

Assistive technology for speech communication encompasses a range of tools and solutions designed to support individuals with speech impairments, facilitating their ability to communicate effectively.
Here are three types of assistive technology specifically tailored for speech communication:
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Devices: AAC devices are tools that assist individuals with limited or no speech in expressing their thoughts, needs, and desires. These devices can range from low-tech options, such as communication boards or picture-based systems, to high-tech solutions, such as speech-generating devices (SGDs) or tablet applications. AAC devices provide a means of communication through symbols, pictures, text, or synthesized speech. They enable individuals to select and convey messages, participate in conversations, and engage in social interactions, enhancing their ability to express themselves and be understood by others.
Text-to-Speech (TTS) Software: Text-to-speech software converts written text into spoken words. It allows individuals with speech impairments to type or select written messages that are then synthesized into speech output. TTS software can be used on computers, tablets, or mobile devices and can be customized to adjust speech rate, voice, and other parameters. This technology enables individuals to communicate verbally by using written words, helping them express their ideas, participate in conversations, and engage in various settings, including classrooms, workplaces, and social situations.
Voice Amplification Devices: Voice amplification devices are designed to enhance the volume and clarity of an individual’s voice. These devices are particularly useful for individuals with soft or weak voices due to conditions such as vocal cord paralysis or certain speech disorders. Voice amplification devices can be portable, wearable, or integrated into hearing aids. They amplify the sound of the user’s voice, making it easier for others to hear and understand them. These devices assist individuals in effectively communicating in various environments, such as classrooms, meetings, or public spaces, without straining their vocal cords.
These are just a few examples of the assistive technologies available for speech communication. Each technology is tailored to address specific communication needs, enabling individuals with speech impairments to express themselves, engage in conversations, and participate more actively in various aspects of life. By leveraging these technologies, individuals with speech impairments can overcome barriers and enjoy improved communication, social connections, and quality of life.
Types of Assistive Technology - Learning, Cognition, and Developmental
Assistive technology for learning, cognition, and developmental support encompasses a range of tools and solutions designed to assist individuals with diverse learning styles, cognitive challenges, and developmental disabilities. Here are three types of assistive technology specifically tailored for these purposes:
Learning Management Systems: Learning management systems (LMS) are digital platforms that facilitate the organization, delivery, and tracking of educational materials and activities. LMS platforms often feature accessibility features, such as text-to-speech, closed captioning, and adjustable font sizes, to support learners with various needs.
They can provide interactive modules, multimedia content, and adaptive assessments, allowing individuals to engage with educational materials at their own pace and in ways that cater to their learning preferences. LMS platforms also enable educators to monitor progress, provide feedback, and customize learning experiences for students with cognitive challenges or developmental disabilities.

Cognitive Assistive Software: Cognitive assistive software applications are designed to support individuals with cognitive impairments by enhancing their attention, memory, organization, and problem-solving skills. These software solutions may include mind-mapping tools, digital organizers, task schedulers, and memory aids. They provide visual cues, reminders, and prompts to help individuals stay organized, manage time effectively, and break down complex tasks into manageable steps.
Cognitive assistive software promotes independence, boosts productivity, and assists individuals in overcoming cognitive challenges in educational, vocational, and daily living contexts.
Communication and Social Skills Apps: Communication and social skills apps are designed to enhance social interaction, language development, and communication skills for individuals with developmental disabilities, such as autism spectrum disorder. These apps often employ visual supports, social stories, and visual schedules to facilitate understanding, social engagement, and communication. They may include features like picture exchange communication systems (PECS), symbol-based communication boards, or speech-generating capabilities.
Communication and social skills apps offer interactive, user-friendly interfaces that encourage practice, support language development, and improve social interactions, enabling individuals to connect with others and express themselves effectively.
These examples demonstrate the diverse range of assistive technologies available for individuals with learning, cognition, and developmental challenges. These technologies are tailored to address specific needs, support learning and skill development, and promote inclusion and independence in educational and social settings.
By leveraging these assistive technologies, individuals can overcome barriers, maximize their potential, and participate more actively in academic, vocational, and social environments.
Types Of Assistive Technology - Mobility Seating & Positioning
Assistive technology for mobility, seating, and positioning encompasses a range of devices and solutions designed to enhance mobility, provide proper support, and improve the overall positioning and comfort of individuals with mobility impairments. Here are three types of assistive technology specifically tailored for these purposes:
Wheelchairs: Wheelchairs are one of the most common and essential assistive devices for individuals with mobility impairments. They come in various types, including manual wheelchairs, power wheelchairs, and specialized models for specific needs. Wheelchairs provide individuals with the ability to move around independently, facilitating access to different environments and promoting participation in various activities. Advanced features such as tilt-in-space, recline, and customizable seating options ensure optimal positioning, pressure relief, and comfort.
Mobility Aids: Mobility aids encompass a wide range of devices designed to support individuals with mobility impairments while walking or standing. Examples include canes, crutches, walkers, and rollators. These devices provide stability, support weight-bearing, and assist with balance. They enable individuals to navigate their surroundings, improve safety, and increase independence in their daily activities. Mobility aids can be customized to fit individual needs, with options such as adjustable heights, wheels, and accessories for added functionality.
Adaptive Seating and Positioning Systems: Adaptive seating and positioning systems are designed to provide individuals with proper postural support, stability, and comfort while sitting or lying down. These systems are commonly used in wheelchairs, specialized seating systems, and other assistive devices. They may include features such as contoured cushions, adjustable backrests, lateral supports, and positioning belts. Adaptive seating and positioning systems ensure
proper alignment, reduce the risk of pressure sores, and enhance functional abilities and participation in activities.
These examples demonstrate the diverse range of assistive technologies available for individuals with mobility impairments. Each technology is tailored to address specific needs, promote independence, and enhance comfort and functionality. By utilizing these assistive technologies, individuals can overcome barriers, improve mobility and positioning, and lead more active and engaged lives.
Types of Assistive Technology - Daily Living Aids
Assistive technology for daily living aids encompasses a variety of devices and solutions designed to support individuals with disabilities in performing activities of daily living (ADLs) and promoting independent living. Here are three types of assistive technology specifically tailored for daily living aids:
Adaptive Tools for Self-Care: Adaptive tools assist individuals with disabilities in tasks related to self-care, such as dressing, grooming, bathing, and eating. Examples include dressing aids like button hooks, zipper pulls, and elastic shoelaces, which make it easier for individuals with limited dexterity to manipulate clothing fastenings. Adaptive utensils with modified handles or built-up grips help individuals with hand weakness or limited mobility to hold and use cutlery effectively. Bathing aids like long-handled sponges or shower chairs provide stability and accessibility while bathing. These adaptive tools enable individuals to maintain their personal hygiene and engage in self-care activities independently.
Home Accessibility and Environmental Control Systems: Home accessibility solutions aim to enhance the accessibility and usability of living spaces for individuals with disabilities. These may include ramps, stairlifts, grab bars, and handrails to facilitate safe and independent mobility within the home. Environmental control systems enable individuals to control various aspects of their environment, such as lighting, temperature, and appliances, through voice commands, remote controls, or mobile applications. These technologies promote convenience, safety, and independence by allowing individuals to modify their home environment to meet their specific needs.
Medication Management Devices: Medication management devices help individuals with disabilities in organizing and taking their medications correctly and on time. Pill organizers with compartments for each day and time of the week assist in sorting and planning medication doses. Automated pill dispensers dispense medications at pre-set times, providing reminders and alerts to ensure medication adherence. Some devices can also connect to mobile applications or caregiver portals, allowing family members or healthcare providers to monitor medication compliance. These devices improve medication safety, prevent missed doses, and support individuals in maintaining their health and well-being.
These examples highlight the assistive technologies available as daily living aids. Each technology is designed to address specific challenges individuals with disabilities face in their daily activities, promoting independence, safety, and overall well-being. By utilizing these assistive technologies, individuals can overcome barriers and actively engage in their daily routines and tasks.
Benefits Of Assistive Technology - Improved Independence
Assistive technology offers a range of benefits, and one of the significant advantages is the improvement of independence for individuals with disabilities. Here are three key ways in which assistive technology promotes independence:
Increased Mobility and Accessibility: Assistive technology, such as wheelchairs, walkers, and mobility aids, enables individuals with mobility impairments to move around independently and access various environments. These devices provide individuals with the freedom to navigate their surroundings, participate in activities, and engage in social interactions without relying on constant assistance. By promoting mobility and accessibility, assistive technology empowers individuals to explore the world around them, pursue their interests, and maintain an active and independent lifestyle.
Enhanced Communication and Expression: Assistive technology plays a crucial role in improving communication and expression for individuals with speech or communication impairments. Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices, speech-generating devices, and communication apps allow individuals to convey their thoughts, needs, and desires effectively. These technologies provide various means of communication, including symbols, pictures, text, or synthesized speech. By using assistive technology for communication, individuals can express themselves, engage in conversations, build relationships, and participate more fully in social, educational, and vocational contexts.
Supported Daily Living Activities: Assistive technology aids individuals in performing activities of daily living (ADLs) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs) independently. Daily living aids, adaptive tools, and home accessibility solutions enable individuals to maintain personal hygiene, dress, groom, prepare meals, and manage household tasks on their own. For example, adaptive utensils, dressing aids, or home automation systems with voice control simplify these activities and reduce dependence on others. By promoting independence in daily living activities, assistive technology enhances self-esteem, autonomy, and overall quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
The improved independence facilitated by assistive technology empowers individuals to live more self-directed lives, make choices, and actively engage in various aspects of daily life. It fosters a sense of empowerment, autonomy, and inclusion, enabling individuals to overcome barriers and participate more fully in society.
Benefits of Assistive Technology - Increased Access To Education & Employment Opportunities
Assistive technology offers numerous benefits, including increased access to education and employment opportunities for individuals with disabilities. Here are three key ways in which assistive technology facilitates access to education and employment:
Accessible Learning Materials: Assistive technology provides individuals with disabilities access to educational materials in various formats. For individuals with visual impairments, screen readers and braille displays convert text into audio or braille, enabling them to access textbooks, articles, and digital content. Captioning and transcription services make audio and video materials accessible for individuals with hearing impairments. By making learning materials accessible, assistive technology ensures that individuals with disabilities can fully engage in educational settings, participate in discussions, and complete assignments, thus promoting equal opportunities for learning.
Accommodations for Assessments: Assistive technology allows individuals with disabilities to access and participate in assessments and examinations on an equal basis. Specialized software and tools assist individuals with reading difficulties, dyslexia, or visual impairments in accessing and comprehending assessment materials. Speech-to-text software and alternative input devices support individuals with motor impairments in completing written assignments or exams. With the help of assistive technology, individuals with disabilities can demonstrate their knowledge and skills in academic assessments and exams, ensuring a fair and inclusive evaluation process.
Assistive Tools for Employment Tasks: Assistive technology enables individuals with disabilities to perform job-related tasks effectively and efficiently. Screen magnification and screen reader software assist individuals with visual impairments in accessing computer applications and information. Voice recognition software allows individuals with mobility impairments or dexterity limitations to control computers and dictate text. Job-specific assistive tools, such as ergonomic keyboards or adapted equipment, support individuals with physical disabilities in performing tasks specific to their occupations. By providing these assistive tools, technology ensures that individuals with disabilities can access employment opportunities, contribute their skills, and succeed in the workplace.
By increasing access to education and employment, assistive technology promotes inclusivity, equal opportunities, and the full participation of individuals with disabilities in society. It helps to break down barriers, overcome limitations, and unlock the potential of individuals, empowering them to pursue educational goals, gain meaningful employment, and thrive in their chosen fields.
Benefits of Assistive Technology - Enhanced Quality Of Life
Assistive technology offers numerous benefits, and one of the significant advantages is the enhanced quality of life for individuals with disabilities. Here are three key ways in which assistive technology contributes to an improved quality of life:
Increased Independence and Autonomy: Assistive technology promotes independence and autonomy by enabling individuals with disabilities to perform tasks and activities on their own. Whether it’s using mobility aids like wheelchairs or walkers, utilizing communication devices for expressing needs, or employing adaptive tools for daily living activities, assistive technology empowers individuals to take control of their lives. This increased independence enhances self-esteem, confidence, and a sense of personal agency, leading to a higher quality of life.
Improved Social Participation and Inclusion: Assistive technology plays a crucial role in facilitating social participation and inclusion for individuals with disabilities. Communication aids, speech-generating devices, and augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) tools help individuals interact with others, express their thoughts, and engage in conversations. Accessible technologies and devices enable individuals to participate in online communities, social media platforms, and virtual spaces, fostering connections and reducing social isolation. By providing equal opportunities for communication and social engagement, assistive technology enhances social relationships, promotes community involvement, and enhances overall well-being.
Enhanced Access to Information and Entertainment: Assistive technology ensures individuals with disabilities have access to information, education, and entertainment on par with their peers. Screen readers, magnifiers, and accessible digital formats enable individuals with visual impairments to access written materials, websites, and digital content. Captioning and audio descriptions make videos and multimedia content accessible for individuals with hearing or visual impairments. These technologies enable individuals to stay informed, pursue educational opportunities, and enjoy a wide range of entertainment options, contributing to a richer and more fulfilling life experience.
By enhancing independence, fostering social participation, and providing access to information and entertainment, assistive technology significantly improves the quality of life for individuals with disabilities. It promotes their overall well-being, empowers them to lead fulfilling lives, and ensures they can actively participate in society.

Comments